In the case of uniaxial stress or simple tension the von mises criterion simply reduces to which means the material starts to yield when reaches the yield strength of the material in agreement with the definition of tensile or compressive yield strength.
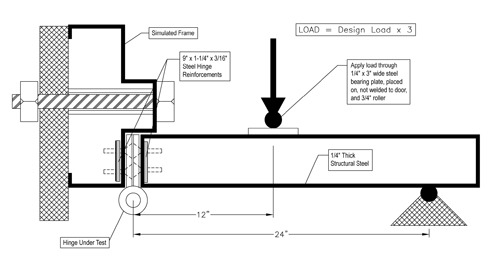
Shear stress of a door hinge solid mechanics.
Similar to average normal stress σ p a the average shear stress is defined as the the shear load divided by the area.
It differs to tensile and compressive stresses which are caused by forces perpendicular to the area on which they act.
A beam can also store energy due to shear stress.
Problem 118 a 200 mm diameter pulley is prevented from rotating relative to 60 mm diameter shaft by a 70 mm long key as shown in fig.
τ v a.
Dividing the shear flow by the thickness of a given portion of the semi monocoque structure yields the shear stress.
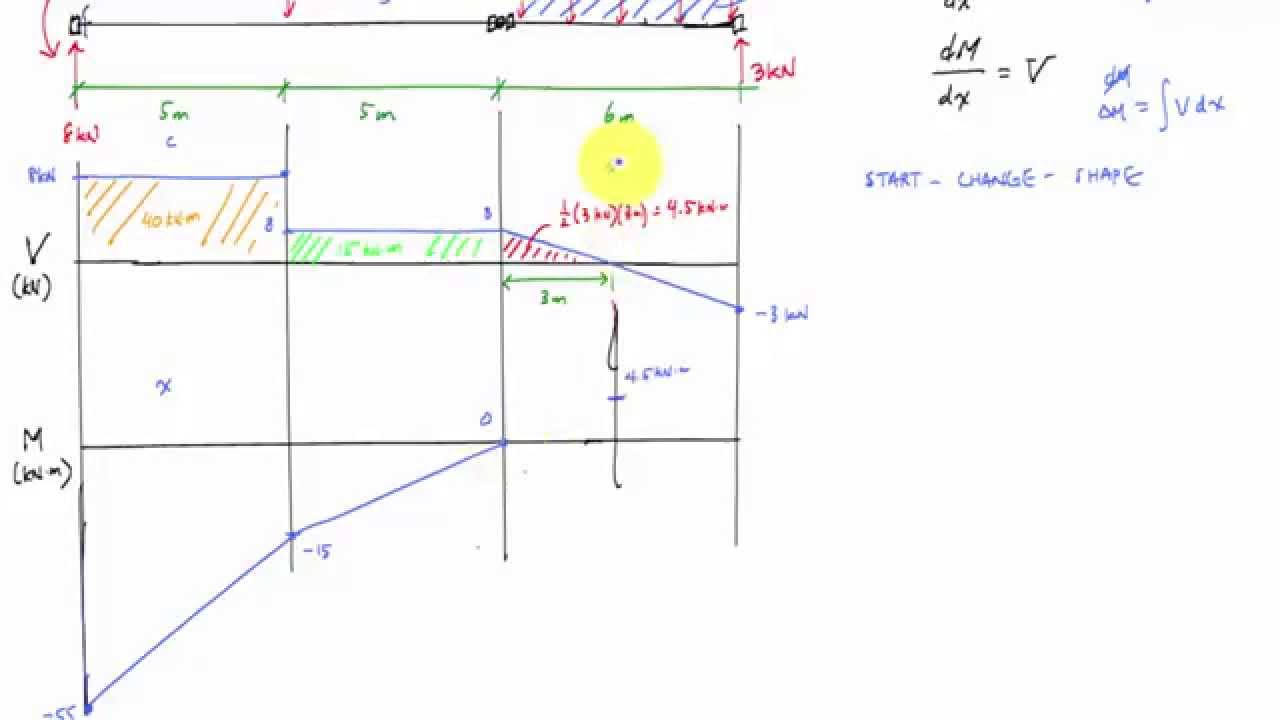
The shear stress component style font family times new roman tau xy at point m in the cross section of the beam at a distance of 1 m from the fixed end is.
One side cannot be under a different shear stress magnitude than the other.
An equivalent tensile stress or equivalent von mises stress is used.
A solid circular beam with radius of 0 25 m and length of 2 m is subjected to a twisting moment of 20 knm about the z axis at the free end which is the only load acting as shown in the figure.
This latter energy is usually much less than that due to the flexural stresses.
Shear stress on element.
If a torque t 2 2 kn m is applied to the shaft determine the width b if the allowable shearing stress in the key is 60 mpa.
Solid mechanics part i kelly245 dx ei m u l 0 2 2 8 2 7 this expression is due to the flexural stress.
Horizontal and vertical shear stress at the same location in a beam.
Multi axial 2d or 3d stress.
Where v is the resultant shearing force which passes through the centroid of the area a being sheared.
However this is not a fixed rule.
Effective normal stress shear stress a 3 b 3 c 1 b 1 a 1 c effective friction angle mohr coulomb envelope line tangent to failure circles c strength envelope intercept typical drained shear strength for overconsolidated fine grained soils or cemented soils.
Shear stress acts on two different parallel surfaces of any element as shown in the diagram at the left.
Forces parallel to the area resisting the force cause shearing stress.