You are looking at the surface expression of many fault lines fault scarp with the hanging wall occupying the valleys and the foot wall representing the plateaus.
Shearing force with hanging wall and foot wall.
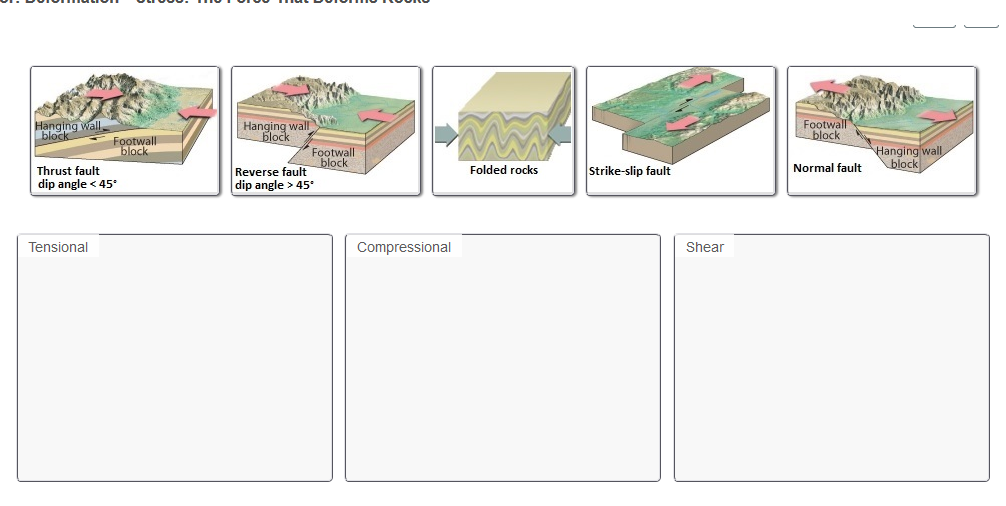
In a normal fault the hanging wall moves downward relative to the footwall.
A downthrown block between two normal faults dipping towards each other is a graben.
E the lower wall below and the hanging wall above c the footwall below and the hanging wall above which type of force is responsible for normal fault formation.
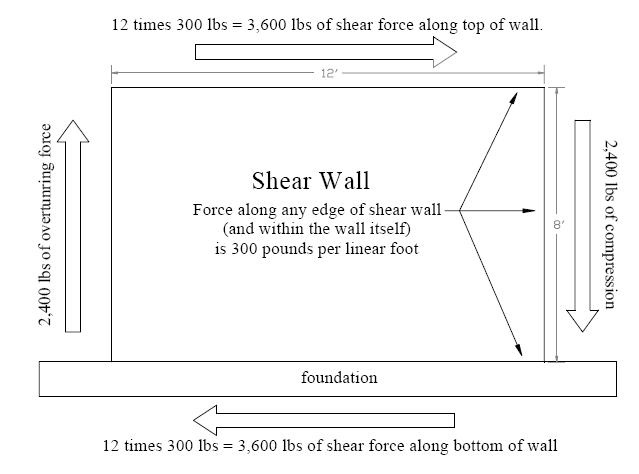
The sheathing panels brace the framing to stop the wall from toppling over and increasing the number of fasteners increases the wall s shear resistance.
Extensional forces those that pull the plates apart and gravity are the forces that create normal faults.
Van der slik s example.
Which type of fault is the scientist observing.
Extensional forces those that pull the plates apart and gravity are the forces that create normal faults.
It is the half of a fault that lies below in a reverse fault.
What kind of faults are present.
It occurs when the fault is at an angle.
Normal faults form when the hanging wall drops down in relation to the footwall.
An upthrown block between two normal faults dipping away from each other is a horst.
Shearing a fault that is formed when compression causes the hanging wall to move over the foot wall is called a n.
Name the letter of each sentence that is true about a hanging wall.
In the same location 38 04 36 00n 109 55 26 61w what would we call these paired.
Shearing a scientist observes a fault where the hanging wall has moved upward relative to the footwall.
The stress force that pushes a mass of rock in two opposite directions is called.
Tension stress compression stress strike slip fault normal fault reverse fault slip past each other with little up and down motion.
The stress force that pushes a mass of rock in two opposite directions is called.
It is the same as a footwall.
Fault is at an angle hanging wall slides downward hanging wall is pushed up and over the footwall.
It slips downward when movement occurs along a normal fault.